Introduction To Singnal & System
What Is this Course All About ?
- Introduction.
- Basic operations on signals.
- Basic system properties.
- Time domain analysis of continuous & discrete time systems.
- Fourier series analysis of CTS and DTS.
- Fourier transform analysis of CTS and DTS.
- Laplace transform.
- Z- transform.
- Sampling.
- Random signals & systems.
What is Signal?
- A signal may be considered as an interruption in a field of constant energy transfer.
- Example: Electromagnetic field of a telegraph circuit, voice signal, video signal.
What is System?
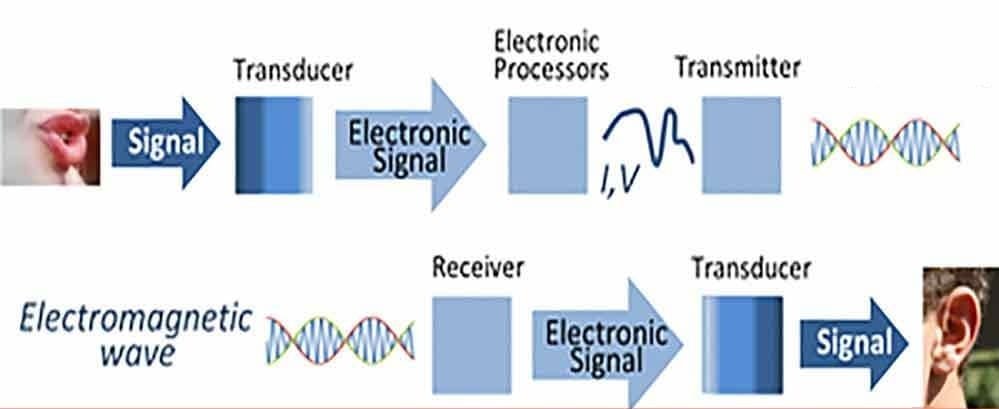
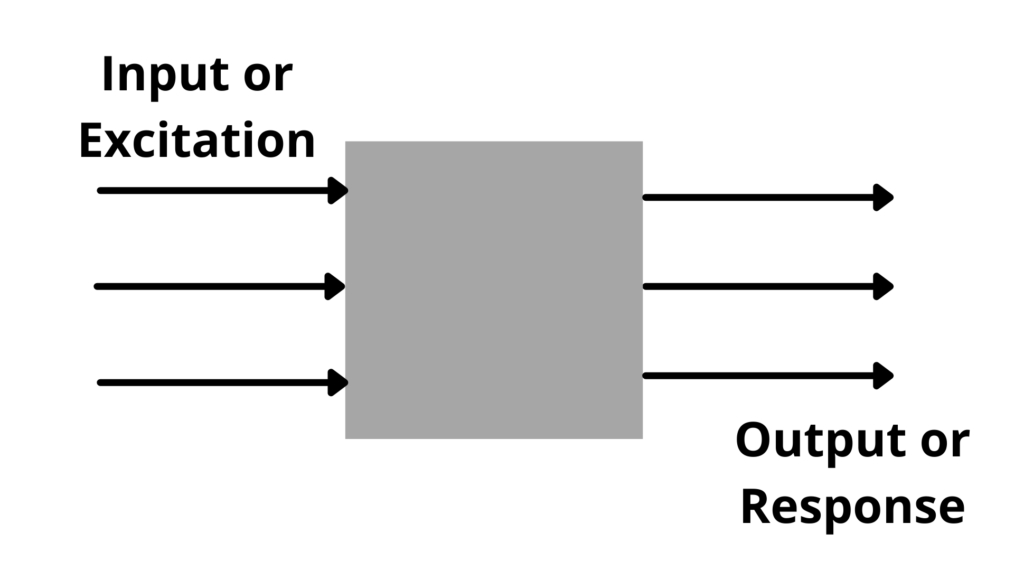
- System is a device or combination of devices. system is a system which describes the information exchange between two points. A system is any process that produces an output signal in response to an input signal.
- Example: Communication System ( transmitter, receiver)
Textbook
- Oppenheim, Alan V., A. S. Willsky. Signals and Systems.
- Video Lecture (Playlist link: https://youtu.be/s8rsR_TStaA )
Quantity which remains same with change in time is a signal. (True/False)
False
Single variable signals depends on more than one variable. (True/False)
False
System alone can't acheive any thing. (True/False)
True
Output signal depends on more number of independent variables as compared to input signal. (True/False)
False



